Abstract
[Introduction] Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is a common viral infection in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT). Early CMV reactivation after allo-SCT is associated with worse non-relapse mortality (NRM) and overall survival (OS). Recently, T-cell replete HLA-haploidentical SCT using post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy-haplo SCT) has been developed and spread rapidly worldwide. Rationale of this strategy is assumed to be selective and cytotoxic depletion of alloreactive T cells which are responsible for graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), while preserving non-alloreactive T cells which can contribute to fight infections. However, recent studies showed that PTCy-haplo SCT was associated with the increased incidence of CMV infection. Letermovir (LET), a novel anti-CMV agent, which inhibits the CMV DNA terminase complex, was approved for the prevention of CMV reactivation in allo-SCT recipients in 2018 in some countries including Japan based on the result of a phase 3 trial. Our facility performs LET prophylaxis in allo-SCT recipient if either donor or recipient is seropositive CMV. Although LET is effective for the prevention of CMV reactivation in allo-SCT recipients, the clinical effectiveness of LET prophylaxis in PTCy-haplo SCT is not well elucidated. Based on these things, we retrospectively evaluated the efficacy of LET prophylaxis in PTCy-haplo SCT.
[Methods] We retrospectively analyzed consecutive 99 recipients who received PTCy-haplo SCT at Hokkaido University Hospital from March 2013 to March 2021. We compared the cumulative incidence of CMV reactivation between the LET prophylaxis group (LET group, 33 patients) and LET non-prophylaxis group (non-LET group, 66 patients). LET was initiated on the day 0 at a dosage of 480mg daily. All patients were monitored for CMV reactivation by using the anti-CMV pp65 monoclonal antibody HRP-C7 assay at least once a week from the time of engraftment. CMV reactivation was defined as the detection of CMV antigen positive cells per 50000 white blood cells, whereas CMV disease was defined by organ dysfunction attributable to CMV.
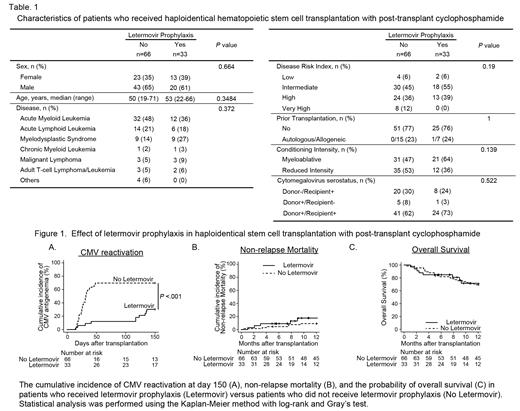
[Results] As baseline patient's characteristics were summarized in Table1, there were no difference between LET and non-LET group in terms of age, sex, underlying disease, disease risk at transplantation, prior transplantation, conditioning intensity, and CMV serostatus. All patients received peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. GVHD prophylaxis consisted of Cy (40-50 mg/kg on day 3 and 4), tacrolimus (from day 5), and mycophenolate mofetil (from day 5). The cumulative incidence of CMV reactivation at 150 days after transplantation in LET group was significantly lower than that in non-LET group (30.3% versus 69.7%; P <.001, Figure1A). Importantly, CMV disease were occurred in three patients without LET prophylaxis (gastritis, enteritis, and retinitis), but not in the patients with LET prophylaxis. The cumulative incidence of NRM at 1 year was similar between the patients with and without LET prophylaxis (17.6% versus 9.2%; P=0.366, Figure1B), as was OS at 1 year (71.5% versus 69.4%; P=0.801, Figure1C). Neutrophil engraftment was achieved in 32 patients (97%) at a median of 15 days in LET group and 64 patients (97%) at a median of 14.5 days in non-LET group (P=0.243). Furthermore, platelet engraftment was achieved in 26 patients (79%) at a median of 34 days in LET group and 57 patients (86%) at a median of 31 days in non-LET group (P=0.282). These findings suggest that LET does not affect engraftment. Interestingly, the length of hospitalization in the LET group was significantly shorter than that in non-LET group (the median, 59.5 days versus 71 days; P=0.0488), suggesting that LET suppresses CMV reactivation leading to early discharge.
[Conclusion] To our best knowledge, this is the largest retrospective study about the efficacy of LET in PTCy-Haplo SCT. LET is effective for prevention of CMV reactivation in PTCy-haplo SCT. Further studies focused on the long term effect of LET prophylaxis in PTCy-haplo SCT, such as the incidence of relapse and chronic GVHD, is warranted.
Nakagawa: AbbVie GK: Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company: Research Funding. Teshima: Gentium/Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Merck Sharp & Dohme: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer Inc.: Honoraria; Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; CHUGAI PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD.: Research Funding; Fuji pharma CO.,Ltd: Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis International AG: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other, Research Funding; TEIJIN PHARMA Limited: Research Funding; Astellas Pharma Inc.: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.: Other; Kyowa Kirin Co.,Ltd.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi S.A.: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal